Can You Reverse Sun Damage? The Comprehensive Guide to Skin Sun Damage Prevention and Treatment
Can You Reverse Sun Damage?
The Impact of Sun Damage on Skin Health and Why Prevention Is Key
Sun damage, also known as photoaging, refers to the harmful effects on the skin due to prolonged exposure to the sun's ultraviolet (UV) rays. UV rays penetrate deep into the skin layers and can cause changes in skin cells leading to premature aging and an increased risk of skin cancer. The visible symptoms of sun damage can include wrinkles, fine lines, age spots, uneven skin tone and a leathery texture. While the skin possesses some natural defences against UV damage, these defences can be overwhelmed by excessive sun exposure, leading to the damaging effects of photoaging.
How does Sun Damage occur?
Sun damage occurs when the skin is exposed to ultraviolet radiation from the sun. UV radiation can penetrate deep into the skin and cause changes in skin cells, including mutations that can lead to cancer. This type of exposure over time also weakens the body's natural defences against UV rays, creating a cycle in which photoaging worsens with continued unprotected exposure.

Consequences of Photoaging
The implications of photoaging extend beyond aesthetic concerns, significantly impacting the health and function of the skin.
Chronically sun-damaged skin often presents a rough, dry texture and a blotchy appearance, characterized by a mix of hyperpigmented (dark) spots known as 'sun spots' or 'age spots' and hypopigmented (light) areas.
The elasticity of the skin is considerably reduced, leading to sagging and the development of deep wrinkles. A striking consequence of photoaging is the development of actinic keratoses – rough, scaly patches on the skin, which have the potential to progress into skin cancer. Moreover, cumulative sun damage also weakens the skin's ability to heal, increasing the likelihood of persistent wounds and infections. It is crucial to understand that while these changes might seem gradual and harmless initially, the long-term health implications of photoaging are severe and should not be overlooked.
What is Sun Damage?
Definition and Effects of Sun Damage
Sun damage, scientifically termed as solar elastosis, is a process where the skin undergoes changes under the impact of the sun's UV rays. This damage primarily manifests as the degradation of the skin's connective tissue - collagen and elastin - leading to a loss of structural integrity and elasticity. Consequently, the skin ages prematurely, a condition known as photoaging.
The effects of sun damage are multifaceted, influencing both the aesthetics and health of the skin. On the surface, sun damage exhibits as wrinkles, fine lines, sun spots, and a rough, leathery texture.
Underneath, the skin's essential functions like protection, temperature regulation, nutrient supply, and sensory perception are significantly compromised. The most critical health risk emerging from sun damage is the elevated risk of skin cancers, including basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma and melanoma. Recognizing these outcomes of sun damage is pivotal to understanding the importance of preventative care and damage reversal strategies.

Recognizing the Signs of Sun Damage
Before tackling the reversal of sun damage, it is essential to recognize its signs. While every individual's skin reacts differently to the sun, there are common signs indicating that your skin may be suffering from sun damage.
- Hyperpigmentation: Often referred to as age spots or sun spots, these are darker patches that appear on the skin areas most exposed to the sun. They are a result of the skin producing extra melanin, the pigment that gives skin its colour, in an attempt to protect itself from the harmful UV rays.
- Fine Lines and Wrinkles: Premature aging of the skin, or photoaging, can be observed as fine lines and deep wrinkles. This occurs due to the breakdown of the skin's collagen and elastin fibres from prolonged sun exposure.
- Rough or Leathery Skin Texture: Overexposure to the sun can make your skin feel rough and dry. In extreme cases, it might even assume a leathery texture.
- Redness and Inflammation: Sunburn is a clear indicator of immediate sun damage. Frequent sunburns can lead to chronic skin inflammation, making the skin appear perpetually red.
- Actinic Keratoses: These are small, rough, or scaly spots that may be pink, red, or brown. They are usually found on areas of the skin that receive a lot of sun exposure and could potentially develop into skin cancer.
- Uneven skin texture /tone: This can occur when the melanin in the skin is unevenly distributed, leading to an inconsistent skin color.
- Liver spots: Sun exposure can increase your risk of skin cancer, particularly if you have fair skin or lighter skin tones. Sun damage is also the main cause of liver spots, which are clusters of flat, pigmented areas that appear on the face, hands, and other areas commonly exposed to the sun.
To reduce your risk for developing these dark spots due to photoaging, it is important to effectively protect your skin from the sun’s harmful UV rays. Sunscreen with a minimum SPF of 30 should be applied daily and reapplied every two hours or more frequently if swimming or sweating. Additionally, wearing protective clothing such as long-sleeved shirts and wide-brimmed hats can help shield the skin when outdoors.
If you notice any of these signs, it would be wise to consult with a dermatologist for a professional evaluation and to discuss potential treatment options. The earlier the detection, the higher the chance for successful reversal of sun damage.

Can Sun Damage Be Reversed? How Can We Reverse Sun Damage?
The question of whether sun damage can be completely reversed is a complex one. While certain signs of sun damage such as hyperpigmentation, fine lines and uneven skin tone can be significantly improved with treatments, the complete reversal of all sun damage effects is currently beyond the scope of modern dermatology. However, combining treatments with a rigorous sun protection routine can mitigate future damage and improve the skin's overall condition.
In essence, while we can minimize the visible signs of sun damage and restore some of the skin's healthy functions, total reversal remains challenging. The skin, once damaged, cannot revert entirely to its initial pre-damaged state. Nevertheless, advancements in skincare science are constantly improving our ability to treat and prevent sun damage, making a future with more definitive reversal techniques possibly within reach.
It's important to approach sun damage with a realistic mindset. Aim for improvement rather than complete reversal and remember that consistent prevention is as important, if not more so, than treatment.
Always consult with a dermatologist for a personalized skincare and sun protection regimen, as individual needs can greatly vary.
The science behind skin regeneration and repair
The science behind repairing skin damage is a complex one. Generally speaking, when the skin experiences sun damage it goes through multiple physiological and biochemical processes that lead to its deterioration. The most common effect of photoaging is collagen degradation, which results in the appearance of wrinkles and fine lines on the skin. Other effects include increased pigmentation, inflammation, redness and DNA damage.
When attempting to reverse the effects of sun damage, our goal is to stimulate the skin’s natural repair mechanisms and boost its regenerative response. This can be achieved through topical skincare products and treatments such as chemical peels, laser resurfacing, microdermabrasion, dermabrasion, cryotherapy and more.
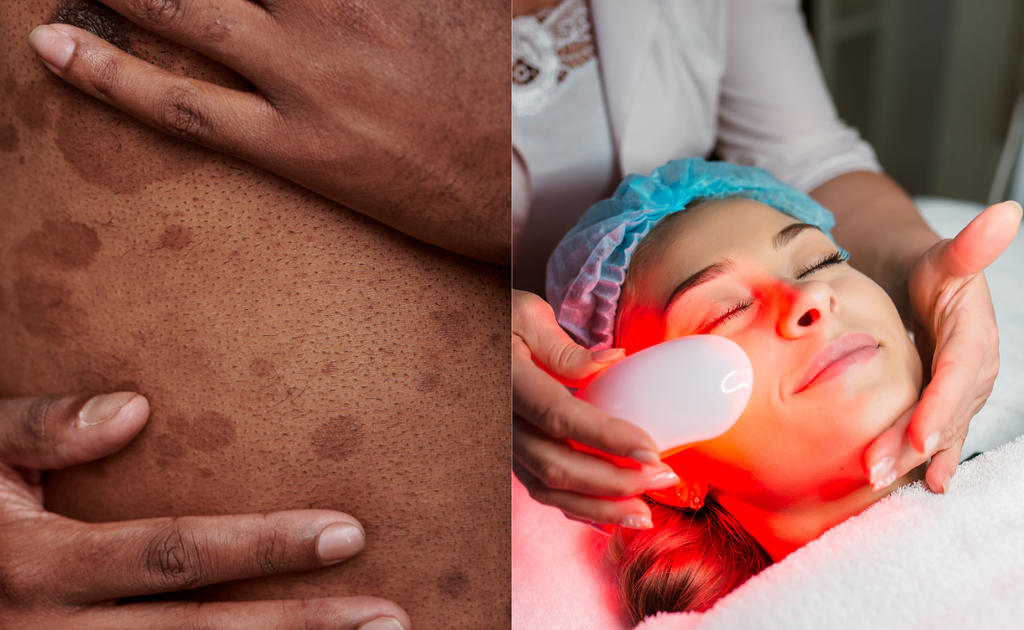
Treatments Available to Reverse Sun Damage
While prevention is the best strategy against sun damage, several treatments have been developed that can effectively reverse its effects. These treatments range from topical creams and oral medications to non-invasive procedures and cosmetic surgeries.
- Topical Treatments: Topical creams containing retinoids, vitamin C, and alpha hydroxy acids can help manage sun damage by promoting skin cell turnover, reducing hyperpigmentation and stimulating collagen production. Hydroquinone and azelaic acid can be used to treat hyperpigmentation specifically. Always consult a dermatologist for the best topical treatments suitable for your skin type and sun damage level.
- Oral Medications: Oral antioxidants like Polypodium Leucotomos extract can help protect against the harmful effects of the sun’s rays when taken in conjunction with topical sunscreens.
- Chemical Peels: Chemical peels involve the use of a chemical solution to exfoliate the damaged outer layers of the skin, revealing healthier, fresher skin beneath. They can reduce the appearance of sun spots, fine lines, and wrinkles.
- Laser Treatments: Laser resurfacing treatments, such as Fraxel and IPL (Intense Pulsed Light), can help minimize wrinkles, uneven skin tone and other signs of sun damage by removing the outer layer of skin. These treatments encourage the growth of new, healthier skin cells.
- Microdermabrasion and Dermabrasion: These procedures involve the removal of the top layer of the skin using a special device. This stimulates the production of new skin cells and collagen, resulting in improved skin texture and tone.
- Cryotherapy: Cryotherapy uses extreme cold to freeze and remove sun spots and actinic keratoses. However, this treatment should only be performed by a professional due to the risk of skin damage.
Remember, it's never too late to start taking care of your skin. If you suspect that you have sun damage, it's best to consult a dermatologist who can provide a personalized treatment plan based on your particular needs.
While these treatments can significantly improve the appearance of sun-damaged skin, ongoing sun protection is essential to prevent further damage and maintain the results achieved.

Natural Ways to Reverse Sun Damage
In addition to professional treatments, there are several natural remedies that can help reverse sun damage. These include:
- Eating a healthy diet rich in antioxidants and vitamins A, C and E.
- Drinking plenty of water to keep your skin hydrated and supple.
- Applying aloe vera gel or honey directly to the skin to soothe inflammation and reduce hyperpigmentation.
- Wearing protective clothing when outdoors, such as long-sleeved shirts and wide-brimmed hats.
- Using mineral sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher for daily sun protection.
- Eliminating alcohol consumption and smoking, which can further damage the skin.
By taking a holistic approach to managing sun damage, it is possible to restore the skin's healthy functions and delay the signs of aging. A combination of prevention, natural remedies, and professional treatments can help you achieve and preserve healthier-looking skin for years to come.
In conclusion, while complete reversal of sun damage may be beyond our current capabilities, it is possible to minimize the visible signs and improve skin health through proper sun protection, natural remedies, and professional treatments.
By taking a proactive approach to your skincare routine and treating sun damage in its early stages, you can achieve healthier, more radiant skin with minimal effort.
 Prevention is Better than Cure: Tips for Protecting Your Skin from Sun Damage
Prevention is Better than Cure: Tips for Protecting Your Skin from Sun Damage
The Importance of Sun Protection in Preventing Further Damage
Preventing sun damage is far more effective than trying to reverse it later. This crucial step should be the cornerstone of your skincare routine. The sun's ultraviolet (UV) rays can cause premature skin aging, hyperpigmentation, and even skin cancer. Therefore, diligent sun protection is essential in maintaining skin health and preventing further damage.
Daily application of broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of at least 30 is a must, even on cloudy days, as UV rays can penetrate clouds. It should be applied to all exposed areas of skin and reapplied every two hours, or more frequently if swimming or sweating. Besides sunscreen, other protective measures include wearing UV-protective clothing, a wide-brimmed hat, and sunglasses when outdoors.
Avoiding the sun during peak intensity hours, usually between 10 a.m. and 4 p.m., can also significantly reduce your exposure to harmful UV rays. Seek shade whenever possible during these hours.
Remember, every step taken towards sun protection is a step towards healthier, more youthful-looking skin. No matter your age, it is never too late to start protecting your skin from the sun. Consistent and proper sun protection is the most effective way to prevent photoaging and reduce the risk of skin cancer.
Strategies for Effective Sun Protection
Sun protection goes beyond just applying sunscreen or staying in the shade.

Sun Protection Factor (SPF)
Sun protection factor, more commonly known as SPF, is a measure of the extent to which a sunscreen can protect skin from ultraviolet (UV) radiation. A higher SPF rating indicates greater levels of protection and allows you to stay in the sun longer without risking sunburn or other sun damage.
Here are some comprehensive tips and recommendations to effectively shield your skin from the damaging effects of the sun:
- Choose Broad-Spectrum Sunscreen: Always opt for a broad-spectrum sunscreen that protects against both UVA and UVB rays. These two types of UV light are primarily responsible for sun damage and skin aging.
- Consider Sunscreen Formulation: Sunscreens come in many forms - creams, lotions, gels, sprays and sticks. Choose a formulation that suits your lifestyle and preferences. For instance, a water-resistant sunscreen might be more suitable if you're involved in water-based activities or sports.
- Apply Generously and Reapply: Use enough sunscreen to cover all exposed skin. Most adults need about 1 ounce, or enough to fill a shot glass, to fully cover their body. Reapply sunscreen every two hours, or immediately after swimming or sweating.
- Don’t Forget Unusual Spots: Remember to apply sunscreen to often-overlooked areas like the ears, back of the neck, backs of hands, and tops of feet.
- Protect Your Lips: Use a lip balm or lipstick that contains sunscreen with an SPF of at least 30.
- Opt for Protective Clothing: Wear sun-protective clothing, such as a long-sleeved shirt, pants, a wide-brimmed hat, and sunglasses, when possible.
- Use Extra Caution Near Water and Sand: These surfaces reflect the damaging rays of the sun, which can increase your chances of sunburn.
- Use Sunscreen Even on Cloudy Days: Up to 80% of the sun's UV rays can pass through clouds, so don't let overcast weather fool you.
With these tips in hand, you'll be well-equipped to protect your skin from sun damage, reducing your risk of photoaging and skin cancer, and maintaining healthier, younger-looking skin for longer.
Sun exposure and skin cancer is more likely to affect fair skin than a darker skin tone
It is true that fair skin tones are more likely to be affected by skin cancer due to their lack of natural sun protection.
The risk for those with lighter complexions increases further the longer they stay out in the sun without proper protection such as sunscreen and protective clothing. As a result, it is highly recommended that anyone, regardless of their skin type or complexion, take proper precautions to protect themselves from the sun’s UV radiation.
This includes seeking shade when outdoors, wearing protective clothing and hats, avoiding being out in direct sunlight during peak hours (10am - 4pm), and applying sunscreen regularly with a minimum SPF of 30. Taking these necessary steps can greatly reduce your risk of skin cancer while also preventing premature signs of aging caused.

UV protection can shield from skin pigmentation
Yes, UV protection can help protect against skin pigmentation. By shielding your skin from the sun's ultraviolet rays, you can prevent hyperpigmentation and age spots. As noted earlier, this is best done through the use of broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of at least 30 that is applied generously to all exposed areas of skin.
What can lighten skin pigmentation?
Lightening skin pigmentation can be accomplished in a number of ways. Some natural methods include topical application of lemon juice or vinegar directly onto the affected area, using a paste made from honey and oatmeal, or applying aloe vera on the hyperpigmented spots.
In addition to these natural remedies, there are several medical treatments that can lighten skin pigmentation, such as chemical peels, dermabrasion, laser therapy, and topical creams.
However, it is important to consult with a doctor before trying any of these treatments as they can sometimes cause skin irritation or other side effects. Lastly, proper sun protection is essential in preventing further skin discoloration from UV radiation. By following the protective measures outlined above, you can keep your skin looking healthy and even-toned.
By following these steps, you can significantly reduce the risk of sun damage and photoaging while maintaining healthier, more youthful-looking skin for longer. However, it is important to remember that some sun damage cannot be reversed and prevention is always key when it comes to protecting your skin from UV radiation

Can Potion Organic's Instant Glow Organic Face Serum Help With Sun Damage And Hyperpigmentation?
Instant Glow Organic Face Serum is formulated with Coenzyme Q10 , Aloe Vera & Acmella Oleracea Extract can help to reduce the appearance of hyperpigmentation, age spots and sun damage.
Coenzyme Q10, Aloe Vera, and Acmella Oleracea Extract each play a unique role in combating sun damage and hyperpigmentation. Coenzyme Q10 is a powerful antioxidant that protects the skin from oxidative stress caused by exposure to the sun, thus reducing visible signs of aging including age spots and uneven skin tone. Aloe Vera is renowned for its soothing and healing properties; it aids in skin regeneration and has a lightening effect that can alleviate hyperpigmentation.
Acmella Oleracea, however, is especially effective in treating hyperpigmentation due to the presence of organic compounds that can reduce, prevent and slow down the process. The effectiveness of Acmella Oleracea has been documented in several studies. In 2016, researchers found that Acmella Extract was able to improve hyperpigmentation by up to 75%, making it a powerful and popular tool in the battle against sun damage.
All of these ingredients can be found in high quality skin care products, making it easy to incorporate them into your daily routine. With proper application and use, you should begin seeing results in no time! This can help keep you looking young and radiant for years to come.
